2020 is an election year, and as we get closer to November, we expect this to replace COVID-19 and the recession at the top of investors’ minds. The makeup of Congress may influence stock market performance, and how stocks and the economy perform prior to the election may forecast who will win.
Although all election years feel different, 2020 no doubt may be one of the most unique election years ever. We have a pandemic, a deep recession, extremely heightened partisanship, a mail-in ballot controversy, an unpredictable president, and the oldest presidential candidate ever.
Amazingly, 1940 was the last time the S&P 500 Index was lower during an election year with an incumbent in the White House. Historically, when a president has been up for reelection, it has tended to boost stocks. Stocks were down big in 2008—but President George W. Bush had finished his two terms. It isn’t about Republican or Democrat—it’s about incumbents trying to boost the economy and stock prices by the time voters go to the polls. Some good news on the economy in the coming months or progress toward a vaccine could potentially get the S&P 500 back to positive territory for the year, after being down 30% year to date in March, and it’s possible that may help President Donald Trump’s reelection chances.
We’re often asked if stocks perform better under a Republican or Democratic president. We’d take a different view and point out that stocks have tended to do their best when we have a split Congress [Figure 1]. Markets tend to like checks and balances to make sure one party doesn’t have too much sway.
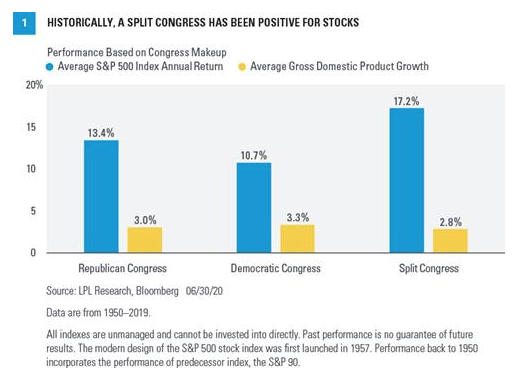
When Republicans have controlled both chambers in Washington, DC, on average the S&P 500 has gained 13.4% per year and gross domestic product (GDP) has grown 3%. When Democrats have controlled both the House of Representatives and the Senate, the economy did a little better, with GDP growth of 3.3%, while the S&P 500 was up 10.7% on average. Some of the best stock gains in recent memory took place under a split Congress. Stocks gained close to 30% in 1985, 2013, and 2019, all under a split Congress. The average S&P 500 gain with a divided Congress was 17.2% while GDP growth averaged 2.8%, again suggesting markets may prefer split power come November.
Watch The Economy
History shows that the U.S. economy has had major bearings on the presidential election outcomes. If there has been a recession during the year or two before the election, the incumbent president has tended to lose. If there were no recession during that time, the incumbent tended to win. Incredibly, the economy has predicted the winning president every year going back to President Calvin Coolidge, when he won despite a recession within two years of the election. But Coolidge inherited a recession when President Warren G. Harding passed away, and by the time people voted in November 1924, the Roaring ‘20s had started to take hold, and the economy was strong again.








