Another Detestable Rally
The bull market in stocks that galloped on for a decade after 2009 was widely described as the most hated rally in history. It took many by surprise (myself included), and came even as money flowed into bonds. Stock markets outside the U.S. behaved roughly as they were supposed to do after a big crash, and traded sideways in a wide range for years. In the U.S., they just went upward. In hindsight, many of us badly underestimated the power and determination of the Federal Reserve.
The current rally is about 10 weeks old, but it may already have taken over as history’s most hated. Again, it is happening in a way that far outstrips previous recoveries from major shocks, and it is doing so despite valuation metrics screaming that stocks are too expensive, and bond yields so low that they imply a comatose economy for years into the future. Having been caught by surprise by the extent of this rally (I can’t deny it) I did my best to be open-minded yesterday, and said that this rally might be justified, if we have a true V-shaped recovery in earnings, and brutal yield curve control by the Fed that somehow doesn’t damage the banks. I made it clear that this was conceivable but unlikely, and that all the risks were to the downside. Judging by the feedback, everybody thinks I was being naively optimistic. If stocks keep rising, as they did Tuesday, this rally will be deeply and darkly detested.
So here are some more reasons to fear further gains for the stock market, in the future. If there is a crucial gauge of “risk-off” sentiment in global markets, it is the dollar. Even if the U.S. is itself the center of the problem, money flows there for sanctuary in times of trouble. A strong dollar in turn makes life much harder for emerging markets with dollar-denominated exposures, and adds to deflationary pressure in the U.S. So it is a sign of clear positivity (or negativity for those of us who hate the rally) that Bloomberg’s dollar index, which compares the dollar to both developed and emerging currencies, has reached its 200-day moving average.
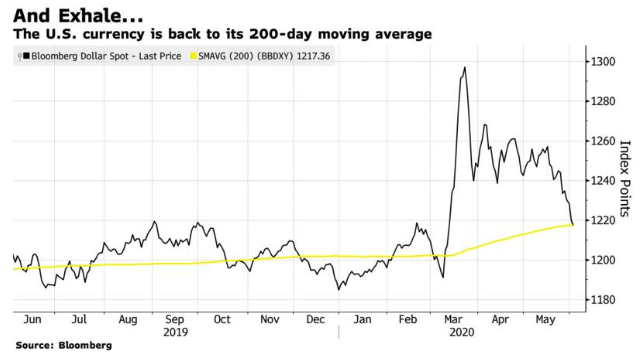
This is a sign that the rally could have more legs. It shows continuing relaxation of tension, with markets behaving as they would if they were positioning for a recovery. And it has a self-fulfilling effect. Brazil appears to be alarmingly positioned to become the next global epicenter of the pandemic, but the Brazilian real has strengthened more than any other currency against the dollar so far this week.
Pathetic Fallacy
London, New York and Hong Kong are all massive market centers and people living there all have reason to view the world negatively at present. In New York, the events of the last few nights have obviated any joy from the easing of social distancing rules in place for the past two months. I visited a doctor’s office close to the Bloomberg office Tuesday, and discovered that store fronts at the bottom of our building, and of all the shops facing it on the other side of Lexington Avenue, had been smashed in. The sight of workers clearing up mountains of broken glass from your place of work, while boards go up along the avenue, isn’t a positive one and won’t put anyone in New York into a bullish frame of mind.
It would therefore make sense if the people living in market centers tend to have a much gloomier prognosis for the future of the pandemic than those outside. This explains the degree of tribalism in U.S. politics, as the overlap between areas worst affected by the coronavirus and those that are politically blue is very close. I know many people who have had Covid, and nobody who has lost their job (although a number of freelancers have seen their income dry up). Millions of people in the U.S. are doubtless exactly the other way around, knowing nobody who has been sick but many who have lost their job.
Is resistance to the rally therefore coming from people living in financial centers who are projecting their experience of the virus on to other areas? I received that suggestion from Brian Alexander of Cypress Capital Management in Vancouver:
I know you can’t travel right now, but honestly if you were able to get out of NYC, you would see that much of the world is coping reasonably well. This is not to gloat or brag as we may have just gotten lucky, but I think much of the media is myopically focusing on NYC and London, which is not reflective of the rest of the world.
In my little neck of the woods—schools are open, restaurants are open with limited capacity as are gyms, stores and pretty much everything else as well. People wear masks when physical distancing is not possible, but other than that you wouldn’t notice much. Basically any indoor gathering of more than 50 people is a no-go, but that is it. Construction never stopped. We weren’t quite as lax as Sweden, but pretty close.
My point is that while the job losses are real, they may well be temporary as people outside of COVID-19 hotspots will not be terrified to leave their homes for long periods of time as the economy opens back up. Residents of Vancouver certainly don’t appear worried to go out and spend.
Much money is controlled by people living outside of Covid hotspots. While I am suitably envious of anyone who gets to live in Vancouver at the best of times, people in such places may be underestimating the risks of what is to come based on their experience to date (just as New Yorkers and Londoners may be overestimating it).
The Spanish flu of 1918, which came in three waves, has framed the discussion of a deeper wave to follow. The following chart, of deaths in the U.S. in 1918 and 1919, is from the Center for Disease Control’s website on the history of pandemics:

If this pandemic follows the same pattern, a V-shaped recovery isn’t going to happen. If a large chunk of people living in Covid-19 hotspots really are mentally exaggerating the possibility that this happens again (and we effectively have a sample size of one for pandemics of equivalent scope in modern history, so the evidence for a second wave isn’t overwhelming), then this rally could indeed be built on stronger foundations than it looks.
So, What Should We Do About It?
The strategy laid out by Ben Inker of Boston-based fund manger GMO LLC in the latest What Goes Up podcast is one that should be taken seriously. Another person who finds it hard to swallow the extreme disconnect between the market and the situation on the streets, he suggests taking a long position in value stocks and balancing it by going short the S&P 500. The logic is that at this point value is likely to outperform in any circumstances. If the V-shaped recovery comes true, then value stocks could rally powerfully. If not, they have sold off so much already that they have less far to fall.
Value has done horrendously compared to the main S&P 500 over the last 12 months, as the following chart shows. Meanwhile, value stocks’ underperformance of the hot Internet stocks in the NYSE Fang+ index has been abysmal:

Does this mean there is a case for shorting the FANGs? History suggests that buying the largest stocks in an index is usually not a good idea. Such stocks have nowhere to go but down, in relative terms. If markets or technology don’t bring them down to size, then the issue becomes whether politicians and regulators will.
The political imbroglios for Facebook Inc. and Twitter Inc. show they are under threat. Even though both services are widely used, they are unpopular. The same is evidently true of Amazon.com Inc., which is unfortunate to be even more unpopular with President Trump. Any incoming Democratic administration would be likely to step up antitrust enforcement.
To bet against the FANGs is to bet that at some point their dominance becomes unsustainable. And if big tech companies’ profitability is any guide, there does look to be a good case for antitrust intervention. The following chart is from Jim Paulsen, veteran chief investment strategist for Leuthold Group LLC:

There are risks involved in betting against companies that keep getting more profitable. But if they keep increasing their margins, and if that is perceived to be at the expense of others, the chances of a long-term antitrust challenge look strong.
And If We Really Have A V-shaped Recovery?
In the event of a strong rebound and ongoing recovery (which I still find unlikely), then value stocks should still shine. We need to be careful with definitions, though. Even in a stronger economy, it is hard to imagine banks doing particularly well, because it is a basic condition of the hopeful scenario that the Fed will keep the yield curve low and flat — terrible conditions for banks. But another group of companies that also tend to show up on value screens might do very well — those with weak balance sheets.

To be clear, such companies are “value” to some (quants who look at value as a factor) and not to others (classic Benjamin Graham-style value investors who want a margin of safety if the worst comes to the worst). The attractive thing about these companies is that they have been ruthlessly sold down by investors since the pre-Covid top in February. In the chart that follows, we can see that Goldman Sachs Group Inc.’s basket of strong balance sheet companies is now higher than it was at the previous peak, while weak balance sheet companies have been stomped on:
Without a strong recovery, many companies with weak balance sheets will fail to raise the cash flows needed to service their debts. Hence their poor stock market performance. But if we really have a V-shaped rebound, prepare to see these companies rip once more. So, if you believe this, find yourself some zombie companies that have leveraged themselves to the hilt, and buy them. If your scenario is right, they should make you a lot of money. And if the idea of doing this makes you queasy, maybe that shows you aren’t quite as confident about an economic resurgence after all.
Survival Tip
Consider moving to Vancouver.
This article was provided by Bloomberg News.