Rotation, Rotation, Rotation
Last November, when excellent vaccine test results sparked a surge in stocks that had suffered most from the pandemic lockdown, it was still possible to doubt whether there had been a true market rotation. The initial drama was followed by a month or two of dithering. That doubt is over. The market is unquestionably going through a major shift. The question is how long it will continue.
Within the stock market, the rotation is most pronounced in the move from “momentum” stocks, which had previously been winning, to “value” companies, which look cheap compared to their fundamentals. That change, by Bloomberg’s measure, is about as violent as any in history:
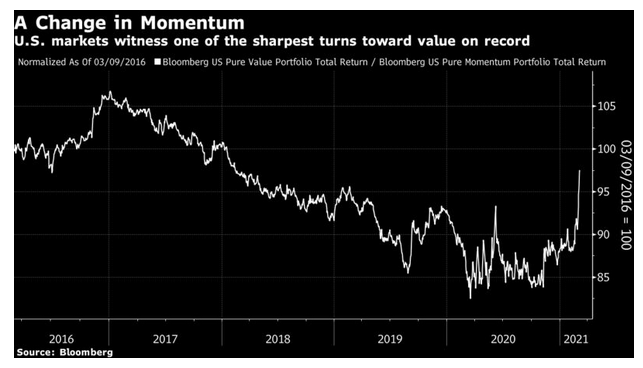
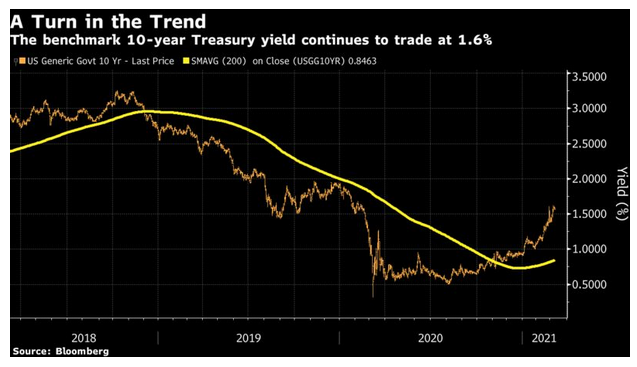
The underlying driver for stocks is the bond market. The rotation toward higher yields in bonds has slowed a little but not stopped, and the benchmark 10-year Treasury yield topped 1.6% again in Monday trading. Its trend now appears to be plainly upward:
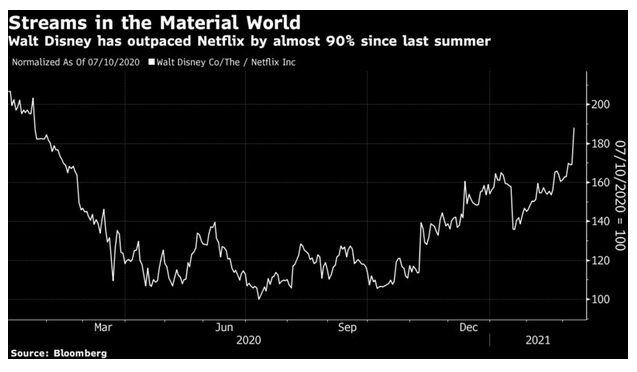
Underlying the move in bonds is a shift in views about the economy, driven in part by the news from Washington that Democrats should be able to push through a $1.9 trillion stimulus package. Meanwhile, there is also excitement over the fight against the pandemic, with the likely reopening date for the economy steadily moving forward. For one dramatic demonstration of this, watch the relative performance since the beginning of last year of Netflix Inc., a pure play on streaming at home, and Walt Disney Co., a bet on streaming content that also comes with a large theme park business. Disney still lags Netflix since the beginning of last year, but has outperformed it by almost 90% since its nadir last July:
So, a rotation is under way. That raises many questions—far too many to answer here. But here are some of the more important issues.
What’s Bubbling?
The question of whether we are in a stock market bubble persists. A lot depends on how to account for the undoubted prop that the market receives from low bond yields. But to an extent, the point of a bubble is that it goes beyond a point where valuation matters; it is already overvalued and the question is how overvalued it can become. That is a question of mass psychology, which can be revealed in stock charts. This is one of those times when looking at patterns in prices can have some relevance.
The greatest fear is that we are staging a repeat of the great dot-com bubble that burst almost exactly 21 years ago. Rather than look at the highly speculative dot-coms that went to market without profits or even revenues to their names, this chart compares the Nasdaq-100, a tech-dominated group of large companies, against the equal-weighted version of the S&P 500, a measure of the performance of the “average stock.” As can be seen, this was a bubble for the ages:
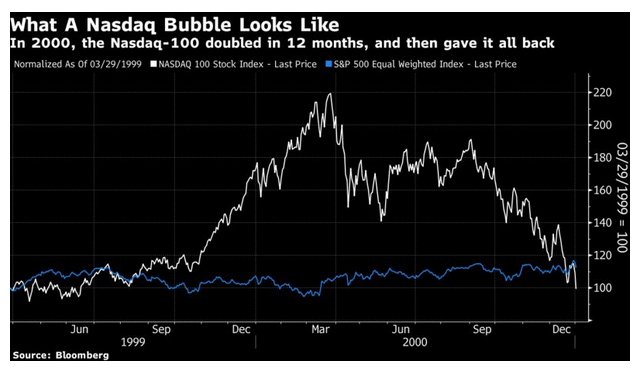
Over the year to the Nasdaq’s peak, the average stock went nowhere. And barely nine months after that, the index had given up all of its gains over the previous 12 months, and was lagging the average stock. Now, this is the same exercise repeated for the year running up to the Nasdaq-100’s high last month:
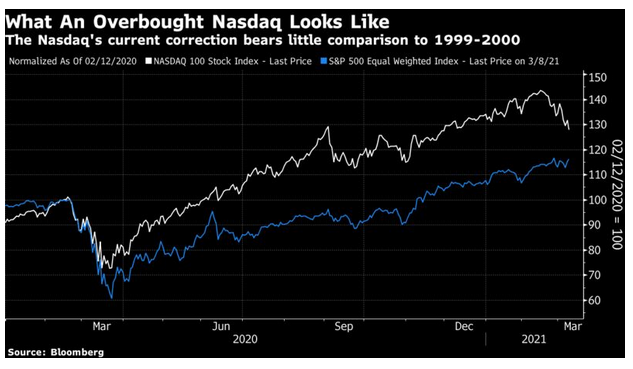
Tech stocks became badly overpriced and are now having a correction that probably has further to go. Meanwhile the equal-weighted S&P 500 is barely below its all-time high. At this level the Nasdaq-100, in behavioral terms, isn’t a repeat of 1999-2000.
However, if we look at the most exciting stock of the moment, the Ark Innovation exchange-traded fund managed by Cathie Wood, we do see a pattern that’s distinctly reminiscent of the internet craze:
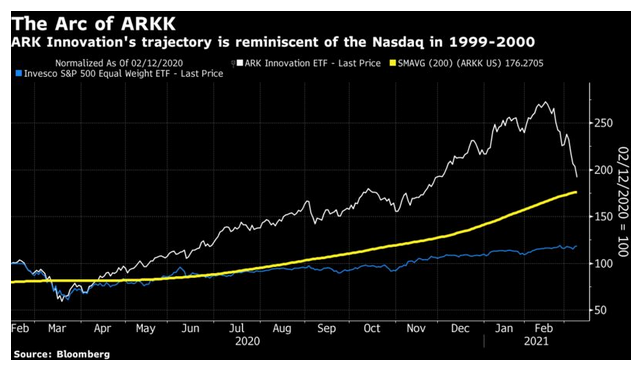
The stocks held by Ark are potential “disrupters” that are for the most part smaller than members of the Nasdaq-100 (Tesla Inc. is a big exception). Wood herself gave a great interview with Bloomberg TV in which she conceded that the market was “broadening,” which is a positive sign of recovering optimism. She also contended that the stocks faring best—such as banks, energy companies and auto manufacturers—are exactly the kind of businesses that stand to be disrupted in the long run by Ark’s investments. These are all valid arguments; buying Amazon.com Inc. in late 1999 proved to be a superlative 20-year investment, even if you had to wait a decade before you broke even. But at this point, the most exciting speculative stocks do look as though they’ve been partying like it’s 1999.
Self-Stabilizers
One point about market rotations is that they come with in-built stabilizers. For example, optimism on growth and fear of inflation leads to higher interest rates, which in turn dampen growth and inflation. This becomes a key question now. Estimates for U.S. growth in 2021 have risen sharply thanks to the success of its vaccine program. Forecasts for many other countries are actively declining due to vaccine disappointment. This means that yields are rising everywhere—but far faster in the U.S. than the rest of the developed world. The following charts from Credit Suisse Group AG demonstrate this nicely:
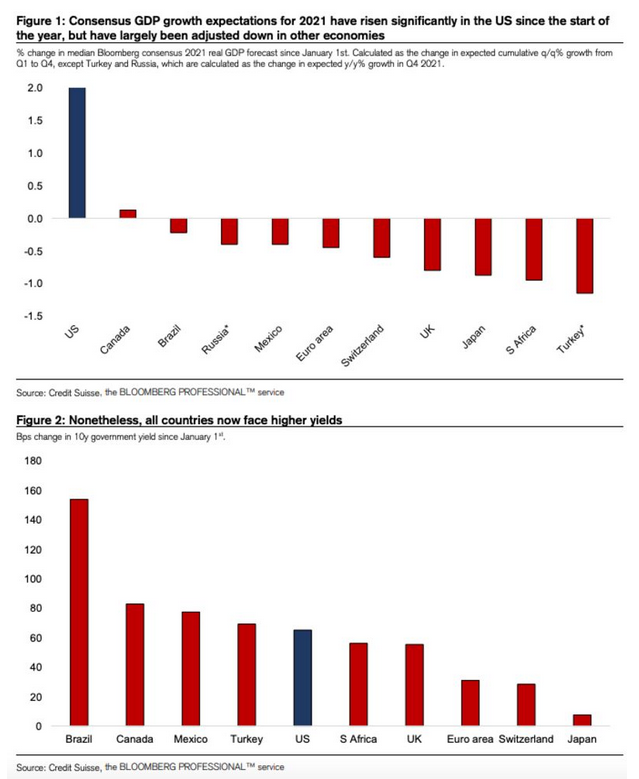
How does this change things? If lots of foreigners pour into Treasuries to take advantage of the higher yields, then the yields won’t rise so much. This was a point that David Tepper, the hedge fund investor who runs Appaloosa Management, made early Monday, to much excitement. That effect hasn’t happened yet. Alternatively, the higher yields in the U.S. succeed in attracting flows that push the dollar up. A higher dollar tends to damp inflation. Over the last four years, there is a distinct tendency for the currency to follow the path set by the gap between U.S. and German bond yields, with a lag of a couple of months. And that is already happening:
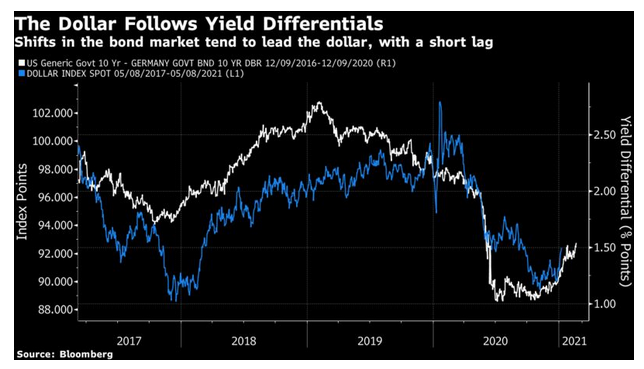
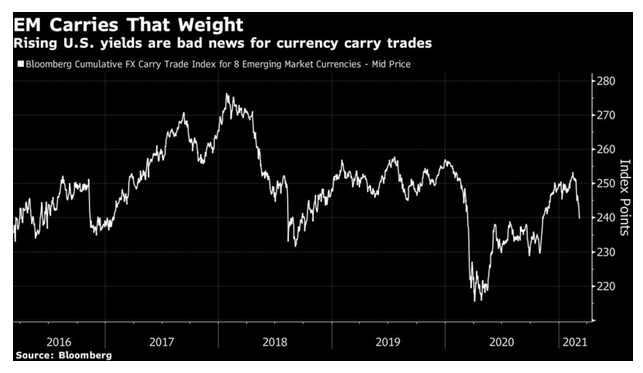
The dollar’s rebound has taken many by surprise, and it could change much of the presiding narrative of a big reflation this year. It could also derail investment in emerging markets. Higher Treasury yields have had their customary effect of messing up emerging market carry trades—the practice of borrowing in currencies with low rates and parking in countries with higher rates, pocketing the carry. A promising rebound for emerging carry trades looks as though it has been snuffed out:
Self-Fulfilling Prophecies
Markets don’t just have their own stabilizers. They also have the ability to make a prophecy and know that it will come true. This could be about to happen in the great rotation between value and momentum.
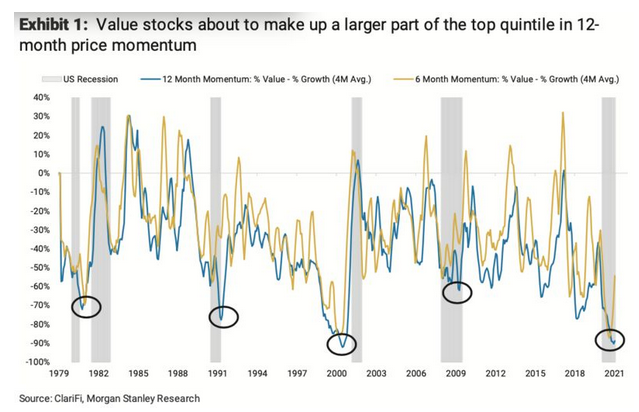
One popular trade among quants is to combine value and momentum. An objection is that the two will tend to cancel each other out, and much of the time they do. But every so often, there is a moment when value stocks have momentum, and the strategy goes into overdrive. Such a moment appears to be at hand.
The following chart is from Mike Wilson, head U.S. equity strategist at Morgan Stanley, who points out that with the anniversary of the great selloff last March, the stocks that appear to have momentum over the last 12 months will change. Rather than being crowded with tech stocks, quants looking to buy “momentum stocks” will instead start to add banks and energy groups. So a rotation that started with a push from economic fundamentals could receive a second wind from technical factors:
This isn’t so much a market stabilizer as a market destabilizer, driven by the weight of money wielded by institutions. This powerful effect could become more disruptive.
The Power Of Bonds
So exactly how much influence do bonds have over stocks? I’d like to mention two interesting angles on this profound question. First, Deltec Bank & Trust Ltd. makes the interesting point that when yields are at very low levels, bond volatility almost by definition gets that much greater when there is any rise. This is the way Hugo Rogers of Deltec puts it:
In a way it is the certainty of ‘low forever’ rates and the unlimited buying potential that is most stimulative.This is reflected in bond volatility. But now that the post COVID recovery has begun, now inflation expectations are justifiably rising, and with fears of another high-teens budget deficit, so is bond market volatility.
This is a foundation of markets, a key component of financial conditions. As long rates rise, as bond market volatility increases, funding tightens. We have explained some of the link to other markets, but the market beyond bonds themselves, that is most effected are equities priced using zero cost of capital (unicorns). It is no surprise to see companies making no cash flow, priced off blue sky thinking, falling fastest in this market. We expect this to continue.
And indeed, if we look at the performance of Ark Innovation, compared with the MOVE index of bond volatility on an inverted scale, there is a family resemblance. While bond volatility appears under control, speculative tech companies do very well; any rise holds them back:
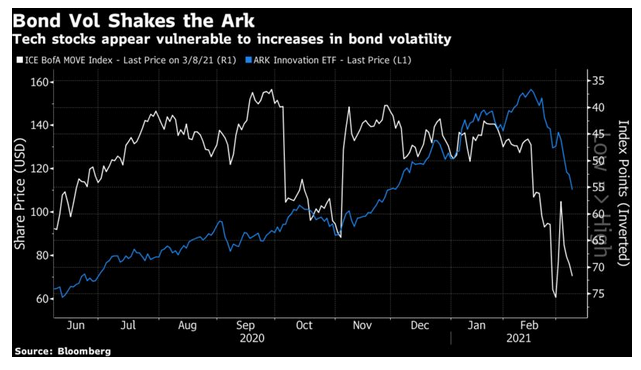
If bond volatility persists, we can expect the difficulties for last year’s leaders to continue too.
What of the broader question of whether lower bond yields justify higher valuations on stocks? It is time for an entry from Robert Shiller of Yale University, who late last year introduced the concept of the “Excess CAPE Yield” (his measure of the long-term earnings yield on stocks minus the 10-year bond yield). The higher this gauge, the more we can expect stocks to beat bonds in future. Thanks to low bond yields, the ECY is positive at present, suggesting that stocks should indeed beat bonds.
At the peak of the boom in 2000, the ECY was negative, meaning that earnings yields had dropped below bond yields, so the indicator correctly signaled that stocks were due for a period of terrible relative performance. The ECY is telling us that the current stock market isn’t as wildly overvalued as in 2000. But that is faint praise. Is it telling us that this is a great time to buy stocks?
Many interpreted it that way. But Shiller wrote a column for the New York Times over the weekend that corrects that impression.
Right now the E.C.Y. is 3.15 percent. That is roughly its average for the last 20 years. It is relatively high, and it predicts that stocks will outperform bonds. Current interest rates for bonds make that a very low hurdle.
Consider that when you factor in inflation, the 10-year Treasury note, yielding around 1.4 percent, will most likely pay back less in real dollars at maturity than your original investment. Stocks may not have the usual high long-run expectations (the CAPE tells us that), but at least there is a positive long-run expected return.
Putting all of this together, I’d say the stock market is high but still in some ways more attractive than the bond market.
Shiller isn’t telling us to fill our boots with stocks, so much as to be very careful about bonds. It’s quite possible for both to fall together. If you find this disappointing, he understands:
The markets may well be dangerously high right now, and I wish my measurements provided clearer guidance, but they don’t. We can’t accurately forecast the moment-by-moment movements of birds, and the stock and bond markets are, unfortunately, much the same.
The bottom line is to continue to be careful out there. We will have to endure plenty more rotation before this is over.
Survival Tips
It has been hard to write this after a day spent largely giving my opinion on the Harry and Meghan interview. Sometimes being a British expat can be a problem. Anyway, on a royal theme, here is a remarkable clip of Prince playing George Harrison's While My Guitar Gently Weeps, in a band that includes Tom Petty and George's own son—who seems thoroughly to enjoy Prince's guitar solo, which comes towards the end of the clip. On a slightly more tenuous royal theme you could sit down and listen to Their Satanic Majesties Request by the Rolling Stones, or Killer Queen by Queen.
If Harry and Meghan's travails have whetted the appetite for even more Windsors drama then my favorite actress in the part of Elizabeth II to date is Helen Mirren in The Queen. She also did a turn as Elizabeth I a year earlier—a rather more dynamic queen who had real and not figurative blood on her hands. Compare and contrast her with another dame, Judi Dench, in the same role in Shakespeare In Love.
John Authers is a senior editor for markets. Before Bloomberg, he spent 29 years with the Financial Times, where he was head of the Lex Column and chief markets commentator. He is the author of The Fearful Rise of Markets and other books.